SpringBoot进阶
SpringBoot进阶
1springboot整合jsp
(1)导入tomcat-embed-jasper依赖
(2)打包方式war,main下新建webapp目录,jsp文件放在这个目录下
(3)全局配置文件中配置前缀和后缀
2springboot整合ssm[本质上就是整合mybatis]
(1)导入mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖 (2.2.2)、数据源、驱动
(2)全局配置文件中配置数据库连接、别名、mapper层日志等级
(3)代码编写同ssm中一样了
补充:springboot整合spring security [如果用到了ss的标签,需要另外导]类似于ssm整合spring security
@Mapper
@MapperScan
环境切换: spring.profiles.active=dev
thymeleaf模板引擎:
(1)先导入依赖 (打包war)
(2)页面放到templates中,引入thymeleaf的命名空间
(3)常用语法: th:text 取数据 @{/}返回当前项目访问名称 th:each 循环 th:if 流程控制
热启 : devtools
一、SpringBoot整合JSP
SpringBoot应用默认支持的动态网页技术是Thymeleaf,同时也支持JSP;因此在SpringBoot应用想要使用JSP需要通过手动整合来实现
1.1、添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<version>9.0.45</version>
</dependency>
<!--按需导-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>1.2、创建JSP页面
修改pom文件打包方式为war; (通常来说,springboot适用于前后端分离模式下的开发情景,)
在
src/main下新建webapp目录;在webapp创建.jsp页面。
1.3、将JSP页面放在webapp中的访问
将JSP文件存放到
webapp目录;在
application.yml文件配置SpringMVC视图解析方式:
spring:
mvc:
view:
prefix: /
suffix: .jsp创建
TestController
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "test";
}
}如果使用静态资源,静态资源需要放在
resource/static目录下。
二、基于SpringBoot的SSM整合(重点)
student 表
(id ,name ,a)
2.1、创建Springboot项目
创建项目时添加依赖
- lombok
- spring web
- mysql driver ,druid数据源
- mybatis framework
- PageHelper
修改mysql驱动的版本(可选)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<version>9.0.45</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version> 版本不要乱写,容易出会话工厂的问题
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>2.2、整合MyBatis所需的配置
完成MyBatis的自定义配置
server.port=8099
server.servlet.context-path=/test
# 配置前缀后缀
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
# 配置连接池
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
# mybatis配置
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.qfedu.bean
# mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml
# 日志 打印sql语句
logging.level.com.qfedu.mapper=DEBUG2.3、创建实体类
Student.java
@Data
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private Integer age;
private String addr;
}2.4、创建Mapper接口及映射配置文件
StudentMapper.java
public interface StudentMapper {
//添加
int add(Student student);
//根据ID删除
int del(Long id);
//修改
int update(Student student);
//查询所有
List<Student> findAll();
//根据ID查询
Student findById(Long id);
}StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.qfedu.mapper.StudentMapper">
<insert id="add" parameterType="student">
INSERT INTO `student`(`name`, `gender`, `age`, `addr`)
VALUES (#{name}, #{gender}, #{age}, #{addr})
</insert>
<update id="update" parameterType="student">
UPDATE `student` SET `name`=#{name},
`gender`=#{gender}, `age`=#{age}, `addr`=#{addr} WHERE `id`=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="del" parameterType="long">
delete from `student` where `id`=#{id}
</delete>
<select id="findAll" resultType="student">
select * from `student`
</select>
<select id="findById" resultType="student">
select * from `student` where `id`=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>2.5、在启动类配置Mapper扫描
@MapperScan
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.qfedu.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSsmApplication.class, args);
}
}2.6、在测试类中测试
package com.qfedu;
import com.qfedu.entity.User;
import com.qfedu.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void test1() {
studentMapper.findAll().stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}2.8、完成学生管理系统SpringBoot版
将之前学生管理系统,相关文件拷贝到项目中,测试。
补充:druid并非是必须导入** :可以在Mapper接口中用@Mapper标记,就不用在启动类@MapperScan**
三、Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是一种类似于JSP的动态网页技术 jsp thymeleaf
动态web技术
模板引擎:JSP、Thymeleaf、Freemarker...【前后端不分离】
3.1、Thymeleaf简介
JSP 必须依赖Tomcat运行,不能直接运行在浏览器中
HTML可以直接运行在浏览器中,但是不能接收控制器传递的数据
Thymeleaf是一种既保留了HTML的后缀能够直接在浏览器运行的能力、又实现了JSP显示动态数据的功能——静能查看页面效果、动则可以显示数据
3.2、Thymeleaf的使用
SpringBoot应用对Thymeleaf提供了良好的支持
3.2.1、添加thymeleaf的starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2.2、创建Thymeleaf模板
Thymeleaf模板就是HTML文件;
SpringBoot应用中
resources\templates目录就是用来存放页面模板的重要说明:
static目录下的资源被定义静态资源,SpringBoot应用默认放行,如果将HTML页面创建static目录是可以直接访问的
templates 目录下的文件会被定义为动态网页模板,SpringBoot应用会拦截templates中定义的资源;如果将HTML文件定义在templates目录,则必须通过控制器跳转访问。
在templates创建HTML页面模板
创建PageController,用于转发允许"直接访问"的页面请求
@Controller @RequestMapping("/page") public class PageController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String index(){ return "index"; } }
3.3、Thymeleaf基本语法 ---->代替jsp
如果要在thymeleaf模板中获取从控制传递的数据,需要使用th标签
3.3.1、在thymeleaf模板页面引入th标签的命名空间
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>这是thymeleaf页面</p>
</body>
</html>3.3.2、th:text
类似于el表达式
在几乎所有的HTML双标签都可以使用
th:text属性,将接收到的数据显示在标签的内容中;标准变量表达式用于访问容器上下文环境中的变量,功能和
EL中的${}相同。Thymeleaf中的变量表达式使用${变量名}的方式获取Controller中model其中的数据。el是jsp中的技术!
<label th:text="${price}"></label>
<div th:text="${str}"></div>
<p th:text="${user.username}"></p>3.3.3、th:object 和 *
选择变量表达式,也叫星号变量表达式,使用
th:object属性来绑定对象。选择表达式首先使用
th:object来绑定后台传来的 User对象,然后使用*来代表这个对象,后面{}中的值是此对象中的属性。 选择变量表达式*{...}是另一种类似于标准变量表达式${...}表示变量的方法,选择变量表达式在执行时是在选择的对象上求解,而${...}是在上下文的变量 Model 上求解,这种写法比标准变量表达式繁琐,只需要大家了解即可。
<div th:object="${user}">
<p th:text="*{id}"></p>
<p th:text="*{username}"></p>
<p th:text="*{addr}"></p>
</div>3.3.4、@{...}
类似于jsp中 $
主要用于链接、地址的展示,可用于:\
<script src="...">;<link href="...">;<a href="...">;<form action="...">;<img src="">.可以在 URL 路径中动态获取数据。
配置项目的上下文路径:
server.servlet.context-path=/statics使用路径表达式:
<script th:src="@{/test.js}"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{/test.css}"/>
<p>
<a th:href="@{/hello/test}">test</a>
</p>
<!-- 传递参数 -->
<p>
<a th:href="@{/hello/test1(id=1, username='zs')}">test</a>
</p>3.4、流程控制
3.4.1、th:each循环
<table style="width: 600px" border="1" cellspacing="0">
<caption>图书信息列表</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>name</th>
<th>addr</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="user:${userList}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.addr}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>3.4.2、分支
th:if如果条件不成立,则不显示此标签
<td th:if="${b.bookPrice}>40" style="color:red">太贵!!!</td>
<td th:unless="${b.bookPrice}>40" style="color:red">太贵!!!</td>
<td th:if="${b.bookPrice}<=40" style="color:green">推荐购买</td>
th:switch和th:case
<td th:switch="${b.bookPrice}/10">
<label th:case="3">建议购买</label>
<label th:case="4">价格合理</label>
<label th:case="*">价格不合理</label>
</td><td th:switch="${user.gender}">
<label th:case="M">男</label>
<label th:case="F">女</label>
<label th:case="*">性别不详</label>
</td>切换: spring.profiles.active=sit
3.5、碎片使用
3.5.1、碎片的概念
碎片,就是HTML片段,我们可以将多个页面中使用的相同的HTML标签部分单独定义,然后通过th:include可以在HTML网页中引入定义的碎片
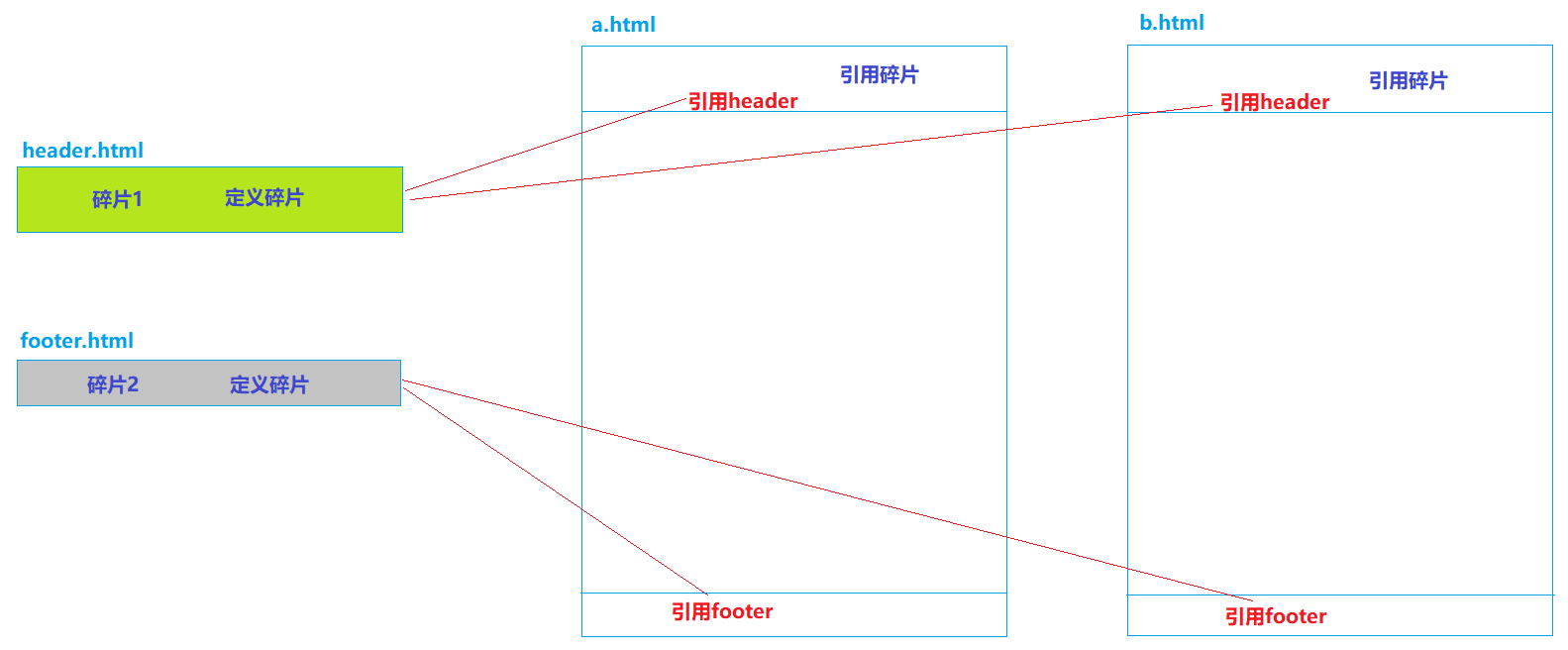
3.5.2、碎片使用案例
定义碎片 th:fragment
header.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="fragment1" style="width: 100%; height: 80px;background: deepskyblue; color:white; font-size: 25px; font-family:文鼎霹雳体">
千锋,六六六!!!
</div>
</body>
</html>footer.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="fragment2" style="width: 100%; height: 30px;background: lightgray; color:white; font-size: 16px;">
千锋教育
</div>
</body>
</html>引用碎片 th:include 和 th:replace
a.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div th:include="header::fragment1"></div>-->
<div th:replace="header::fragment1"></div>
<div style="width: 100%; height: 500px">
定义内容
</div>
<!-- <div th:include="footer::fragment2"></div>-->
<div th:replace="footer::fragment2"></div>
</body>
</html>四、SpringBoot应用的热部署配置
"热" --- 不用停掉现有操作就可以进行“修改”的一种技术。
USB --- 热插拔
PS2 --- 不支持热插拔
4.1、热部署
项目首次部署、服务启动之后,如果应用发生了变化、而且IDEA感知到了应用的变化,就自动的完成jar的更新,无需手动再次启动服务器,就可以访问应用的更新。
目的:提高效率
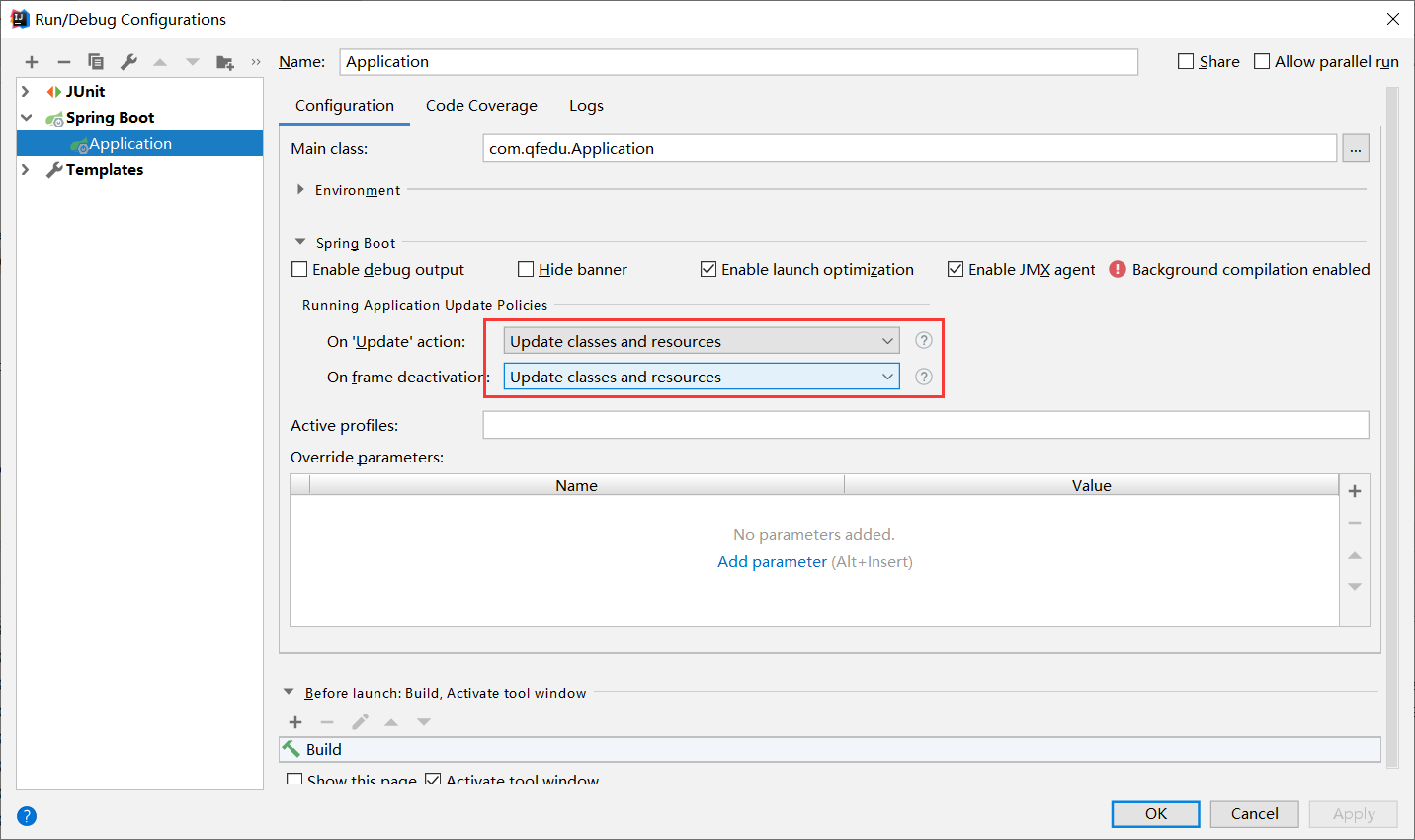
4.2、热部署配置
热部署: devtools jrebel
4.2 .1、IDEA配置
File---settings
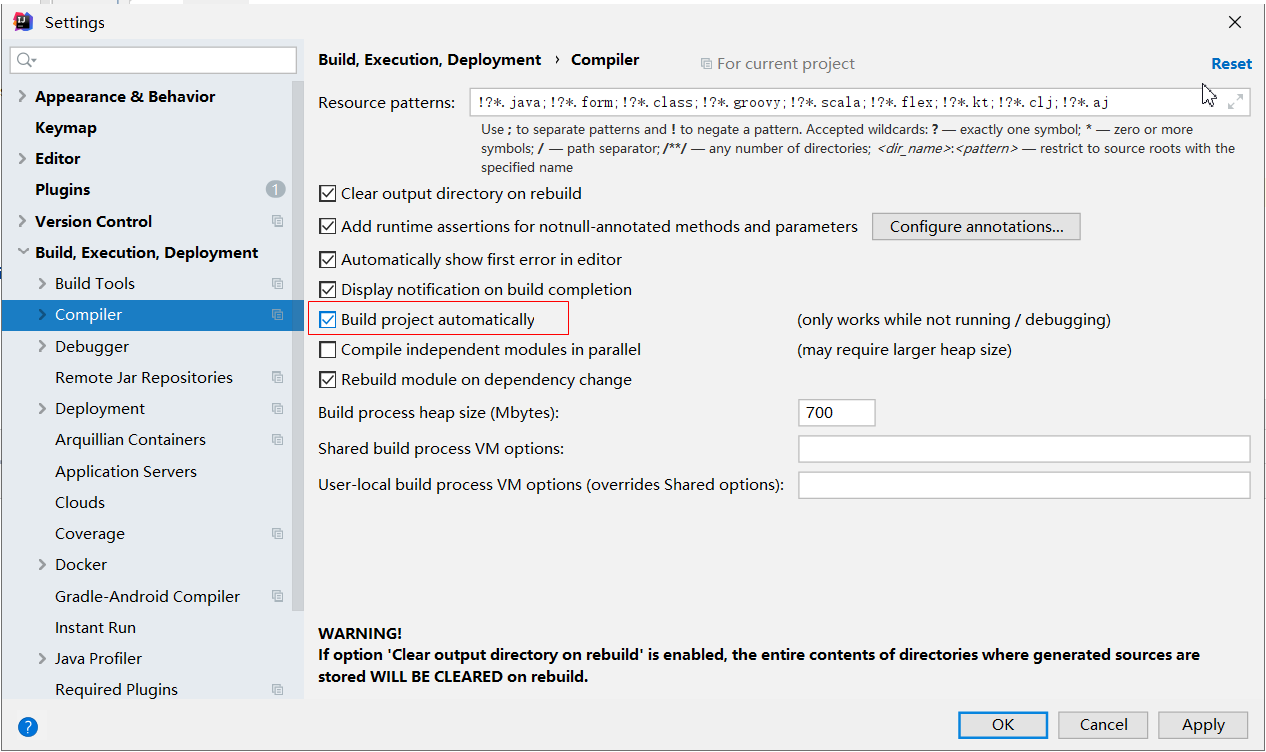
4.2.2、SpringBoot项目配置
在需要进行热部署的SpringBoot应用中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>配置SpringBoot应用的变化更新策略